



Scroll for the full story

Scroll for the full story
SIUE’s Research Centers are engaged in innovative, collaborative projects both on and off campus. They provide educational offerings and offer opportunities to collaborate with our faculty and students on customized projects.
Thanks to decades of advancements in computational technology, we live in an era where it is relatively easy to collect and store data. Yet, making sense of “Big Data” is not always a simple task. The Center for Predictive Analytics is a university-wide research center that serves both the SIUE community and external partners by using and developing state-of-the-art data analysis, machine learning and data visualization techniques to mine complex data for meaningful insights and real-world applications. In addition to supporting the analytical needs of our faculty researchers and industry partners, the Center offers educational and training opportunities in data analytics and machine learning to SIUE students and regional workforce, supports student retention and intervention strategies at the campus level, and promotes the ethical use of data analytics and machine learning through workshops, seminars and conferences.
The SIUE Center for STEM Research, Education and Outreach is a collaborative enterprise among several SIUE academic units, local community colleges and school districts, regional offices of education, and the community at large. The Center’s mission is to develop, strengthen and promote STEM research, education and outreach in the region.
GeoMARC is a research center that is focused on the use of advanced technologies in Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, digital image processing, geospatial automation, and machine learning to help solve a wide range of issues within government, private, institutional, and local communities. The center’s primary goal is to foster cross disciplinary and multi-institutional partnerships in order to develop and promote the use of geospatial technologies to conduct, lead, and influence research and innovation. In addition to research, GeoMARC is actively engaged in providing community and intra-university educational outreach for the advancement of spatial thinking and the evolving uses of geospatial technologies.
The IRIS Center at SIUE is an interdisciplinary facility designed to support individual and collaborative scholarship that applies digital content as a primary methodology. The center's mission is to facilitate cross-disciplinary projects that involve innovative uses of technology in the humanities and social sciences, support these projects with facilities, equipment, and human resources, foster active collaboration between faculty and students, encourage the development of curricular innovation that makes use of digital applications, and promote digital endeavors that intersect with community initiatives.
The NCERC is a nationally recognized research center dedicated to the development and commercialization of biofuels, specialty chemicals and other renewable compounds. The NCERC’s fully functional dry grind pilot plant and laboratories are equipped with advanced biofuels capabilities including corn fractionation, pretreatment, and a fermentation suite with 5, 30, 150 and 1500L scale-up. Facilities are staffed by industry veterans with more than 100 years of collective experience in fermentation and biofuels production. This knowledgeable team has the flexibility and expertise to design and carry out projects in any region of the advanced biofuels or specialty chemicals space.
The Center for Crime Sciences and Violence Prevention (CCSVP) contributes to crime/violence reduction efforts in the region. CCSVP promotes and develops partnerships involved with violence prevention/reduction and works with stakeholders to assist in product/program development and evaluation of crime/violence prevention efforts. CCSVP assists in improving accountability and transparency of all stakeholders in the criminal justice process and serves as a regional clearinghouse for granular criminal justice data, improving access to data across agencies, researchers, and the public.

Scroll for the full story

Scroll for the full story
Fewer than half of children living in the U.S. are part of a traditional nuclear family according to the Pew Research Center. And, yet, gender-specific school and community events, such as father-daughter dances, continue to be the norm. While these events are meant to celebrate family and build connections, they also exclude children who do not fit within the constraints of the event.
“Gender-based guidelines promote exclusion and the marginalization of families with LGBTQ+ parents and children, families with single parents, and many others,” said Emily Love, research assistant at Goshen Education Consulting and two-time SIUE alumna. “These are public events often sponsored by public schools and funded by taxpayer dollars. Given that reality, these events need to be open and fairly accessible to all constituents — not the select few families who fit this outdated and unrealistic norm.”
Love contributed to research on this topic while earning undergraduate and graduate sociology degrees from SIUE in 2020 and 2022, respectively. She worked with Ezra Temko, PhD, assistant professor and applied political sociologist, and student researchers Destiny Baxter, Adam Loesch and Heidi Masching to study primary source data for information about the challenges faced by communities that hold gender-specific events.
Next, the researchers focused on communities that have changed their policies or events to be more inclusive. The researchers conducted more than a dozen in-depth interviews with individuals across the country who were involved in the changes, including school principals and board members, parents, and advocates.
“The most impactful moments for me were hearing from the parents and community members directly affected,” said Love. “Hearing them share their experiences of exclusion, their self-advocacy, and their resilience was both inspiring and heartbreaking. I think it is easy for people to shrug off this issue and see it as something a very small group of people are dealing with. But the truth is, the majority of families in communities across the country would likely need some type of accommodation to attend gender-specific events.”
The research team’s manuscript, “‘You can’t go to the dance because you don’t have a male role model in your life: Heteronormativity, Stigmatization, and Daddy-Daughter Dances,’” has been accepted for publication in “Sociological Focus.” Additionally, the team partnered with the Young Elected Officials Network to publish the policy toolkit “Communities Moving Past the Daddy Daughter Dance: Adapting Gender Inclusive Events for the 21st Century.”
“This topic is personally meaningful to me because I witnessed and experienced the hardship these events can cause,” shared Temko. “When I was in graduate school, my foster daughters brought home invitations to the town's Daddy-Daughter Dance and Mommy & Me Tea through their school. I hope our research will raise awareness about how gender-exclusive events can stigmatize diverse families while also providing communities with tools and resources to adapt their events to be more inclusive.”

Scroll for the full story

Scroll for the full story
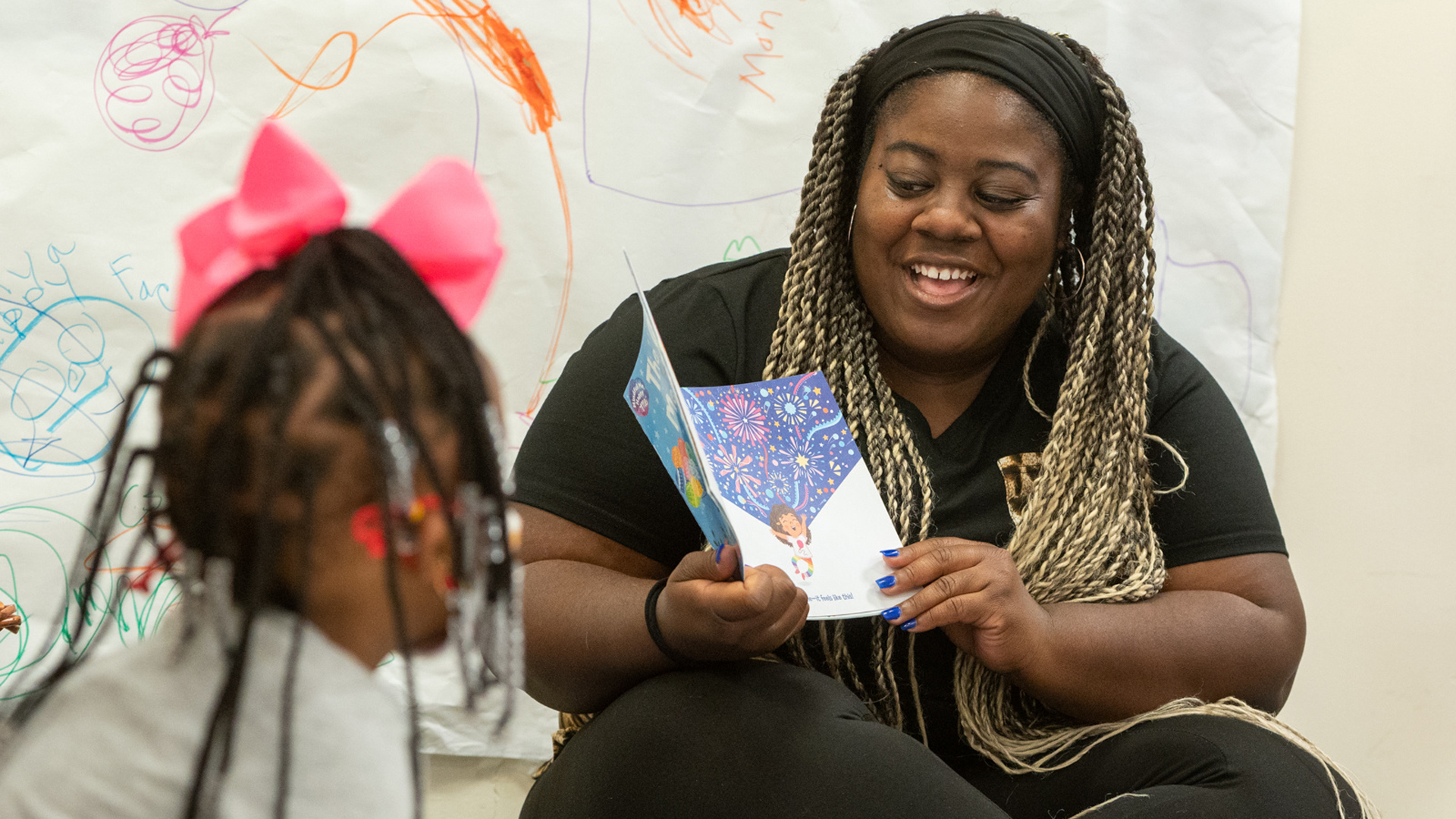
Scroll for the full story
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects openings in the childcare industry will exceed 170,000 per year for at least the next eight years. With a 10% decline in the number of childcare workers across the country as compared to before the COVID-19 pandemic, the industry is in dire need of qualified early childhood educators.
The SIUE School of Education, Health and Human Behavior’s (SEHHB) early childhood education program is working to alleviate some of the stress on this sector. In addition to its traditional pathway to earning a bachelor’s in early childhood education, the SEHHB also offers the Early Childhood On-Site (ECHOS) program for students already working in an early childhood setting. Courses are offered at times and locations convenient for working adults, and additional resources are in place to ensure students are able to successfully complete the undergraduate degree program and earn their teacher licensure.
One support mechanism that was initiated in fall 2022 is the Early Childhood Access Consortium for Equity (ECACE) Scholarship Program, which is administered by the Illinois Student Assistance Commission in partnership with the Illinois Board of Higher Education and the Illinois Community College Board. SIUE received a grant for $937,313* to award scholarships that cover up to the total cost of attendance after other financial aid. The scholarship can be used to cover tuition and fees, room and board, and books and supplies.
“The ECACE funding recognizes and is responsive to the needs of the current early care and education workforce, which are primarily women, including women of color,” said Stacie Kirk, professor, early childhood education program director and co-principal investigator (PI) on the grant. “These are professionals who often are not able to go back to school and increase their education and knowledge base because they need to continue working full time to support their families.”
In addition to providing scholarship opportunities for students, the ECACE program grants third-year status to students who have already completed the Associate of Applied Science (AAS) degree in early childhood education.
“The AAS pathway, along with the scholarship opportunity, creates more feasible opportunities for working professionals to return to school to complete an undergraduate degree and earn teacher licensure,” Kirk explained.
The ECHOS program has always placed significant emphasis on equity and inclusion for its students. Participating in the ECACE program was a natural progression for the SEHHB.
“Our dean, Robin Hughes, PhD, did not hesitate to activate our invested faculty when the ECACE initiative launched,” said Natasha Flowers, PhD, assistant dean for anti-racism, equity and inclusion, and PI on the grant. “With more state-level support for ensuring culturally responsive pedagogy, credentialing more hardworking early childhood educators, and striving to leave no community without available, competent, inclusive early education, SEHHB will not refuse the resources to build on our momentum!”
*This project is supported by the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) through the Illinois Board of Higher Education as part of an award totaling $937,313, of which $937,313 are federal funds with 0% financed with nongovernmental sources. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement by, the DHHS or the U.S. Government.

Scroll for the full story
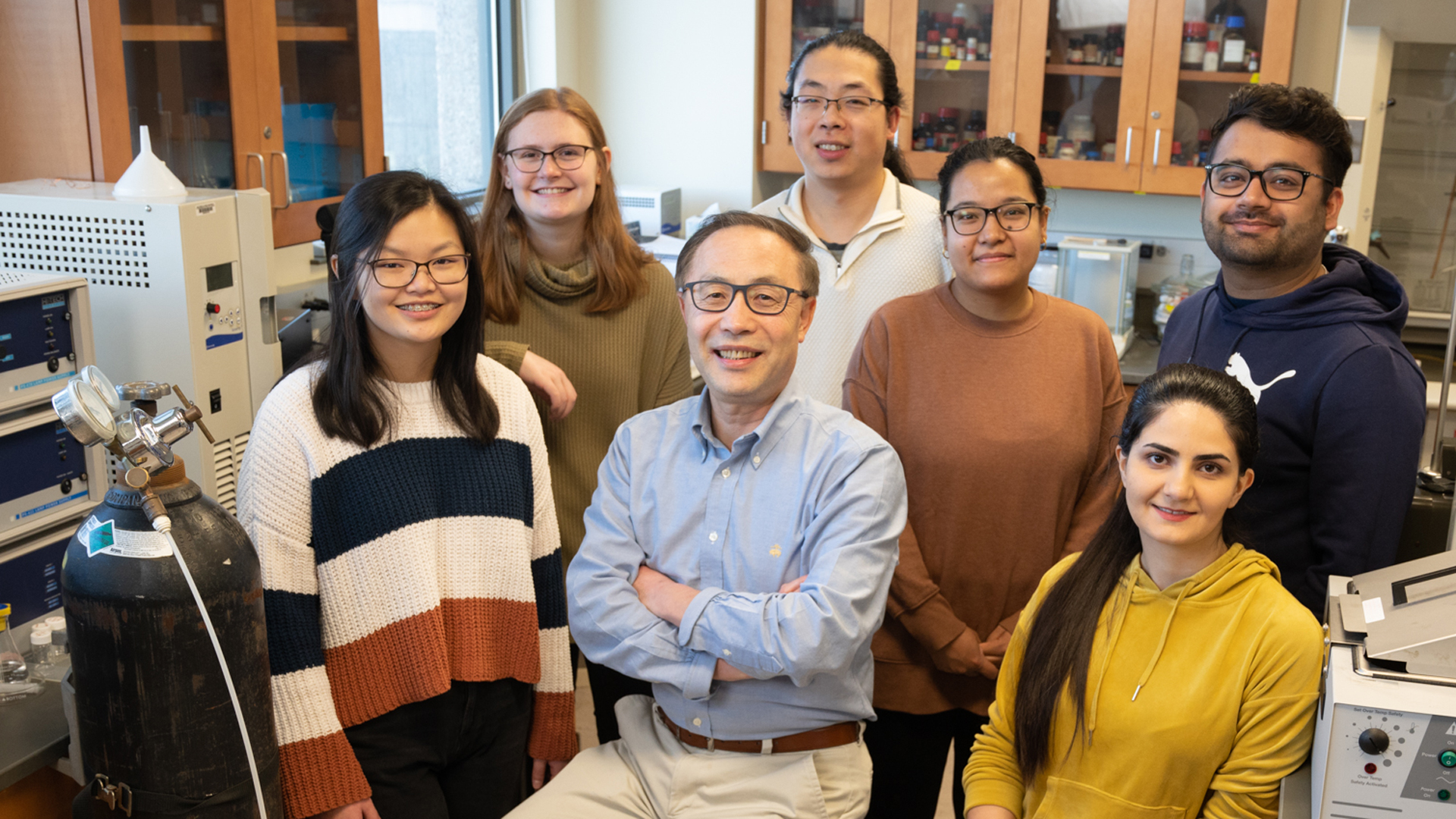
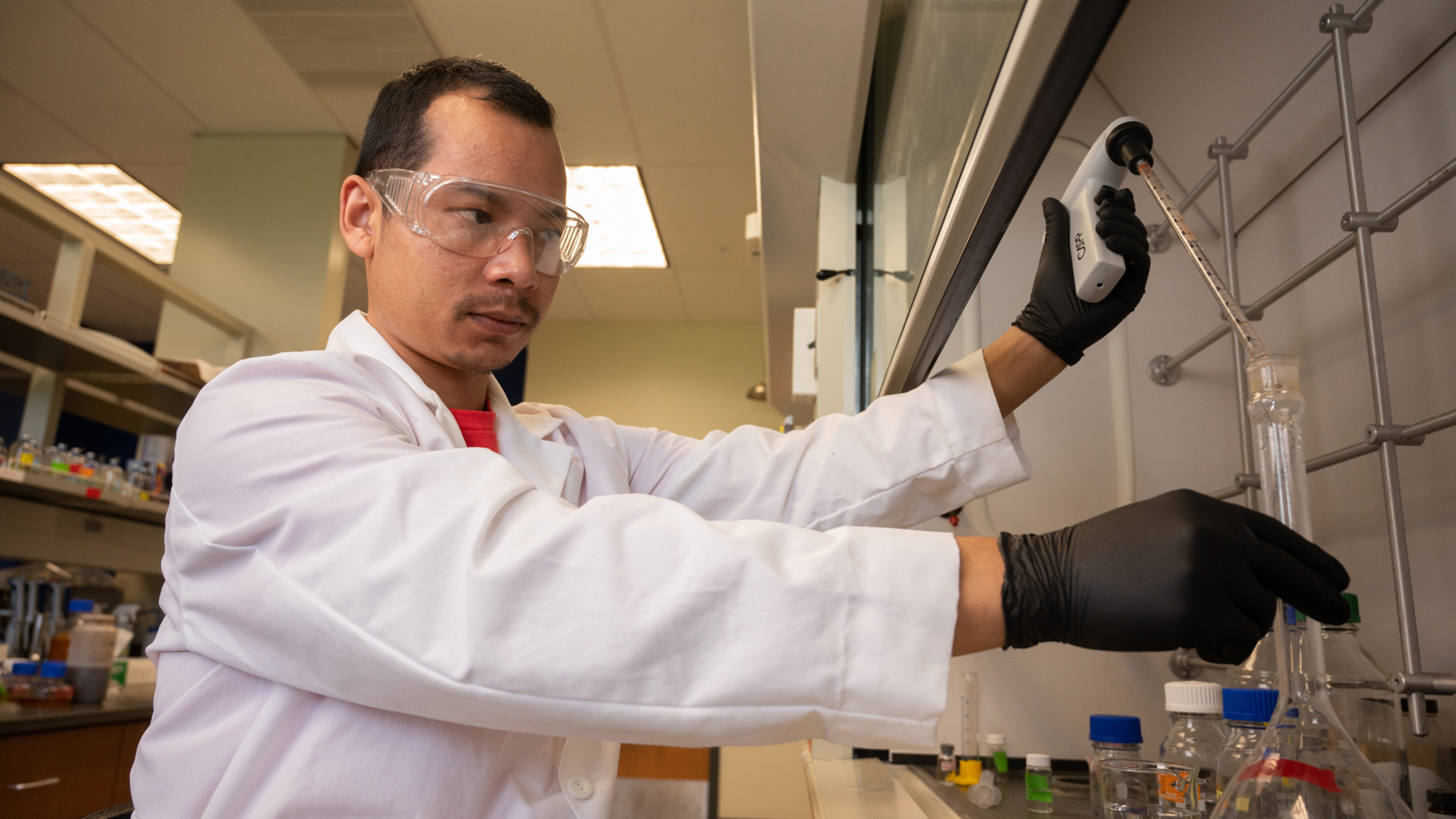
Catalytic power describes an enzyme’s ability to accelerate a chemical reaction. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms at a much faster rate than the corresponding reactions in water, but the origin of their catalytic power is still in question by the scientific community.
“The search for the origin of the enormous catalytic power of enzymes has a long history and has led to many proposals,” said Yun Lu, PhD, professor in the Department of Chemistry. “Understanding the origin of enzymes’ catalytic power can help understand the nature of life, establish catalytic theories for drug design, as well as find biocatalysts to promote useful reactions in industry.”
Lu is working to provide further clarity on the topic through his biomolecular chemical reaction mechanism study funded by a $433,000 grant from the National Institutes of Health*.
“Over the past 20-plus years, the dominant focus on enhanced transition state binding as the origin of enzyme catalysis has given way to the challenging question as to whether there is an active site compressive effect that can help enzymes achieve the huge rate accelerations,” Lu explained.
“In this project, we will design enzyme model reactions and use the same methodologies that enzymologists have begun using to replicate the observations in enzymes in an attempt to provide insight into the questionable physical origin of enzyme catalysis,” he continued. “Our results are expected to help develop theories for enzyme catalysis that can guide future efforts to design efficient drugs and biocatalysts.”
Lu’s team of undergraduate and graduate students is pioneering the use of enzyme model reactions and the kinetic isotope effect technique to study the role of molecular dynamics in the chemical processes. Results are expected to provide insight into the role of protein vibrations in enzyme catalysis. He believes this project will attract significant attention from the scientific community and direct his team’s research for many years to come. It will also provide Lu’s students with valuable research experience that will prepare them to enter a variety of fields following graduation.
"The students will be trained to make chemical compounds, study the chemical properties, operate chemical instruments, and collect, analyze, and discuss scientific data,” said Lu. “With these experiences, the students are prepared to be teachers, problem-solvers for chemical and pharmaceutical companies, and to enter health-related professional schools or PhD programs.”
“We are the first and the only group to use these methodologies to systematically study the enzyme model reactions in solution,” Lu added. “In addition to supporting our students’ research, the grant will also help improve the lab facilities to form a solid infrastructure for our future research."
*This project is supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as part of an award totaling $433,500, of which $433,500 are federal funds with 0% financed with nongovernmental sources. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement by, the NIH or the U.S. Government.

Scroll for the full story
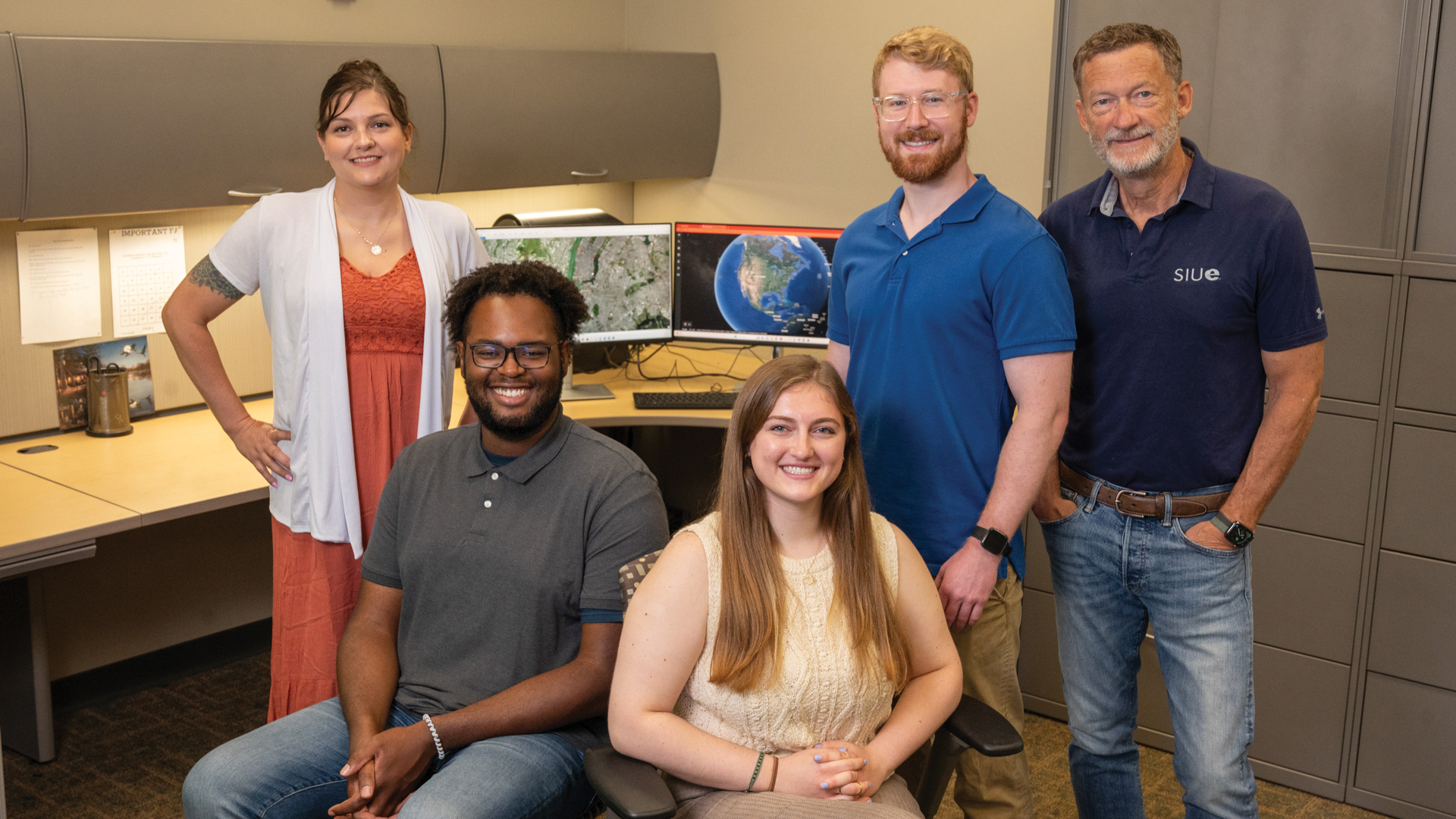
Flooding has become a major issue in the Midwest due to a variety of factors, including changes in land use, slower water infiltration rates and the loss of natural rainwater storage. As a result, communities throughout the region have suffered negative economic and environmental impacts.
Through funding from the Environmental Protection Agency, SIUE partnered with Heartlands Conservancy, and several other local, state and federal entities to study the Prairie Du Pont Creek Watershed located in St. Clair County, Illinois, focusing in the municipalities of Cahokia Heights and East St. Louis. This area has suffered extreme flooding several times in the past decade, leading to repeated structural damage to homes and businesses, water quality concerns, and overwhelming sanitary sewer function, among other issues.
Together, the project team sought to create a long-term watershed plan to address flooding issues, and improve drainage and water quality. This vision involved both technical analysis of existing conditions and public input.
Watch the video.
Rohan Benjankar, PhD, associate professor and graduate program director in the School of Engineering, served as SIUE’s lead researcher on the project. With the support of two SIUE graduate students, Benjankar developed integrated watershed hydrological and hydraulic models to study flood hazard in the watershed and identify the areas at greatest risk for flooding. Modeling is a backbone to develop a strategy for watershed management for the future.
“In order to reduce flooding hazard and improve water quality, it is important to manage water flow within urban areas as well as in the entire watershed,” explained Benjankar.
Using the data collected, along with input from local residents and officials from local, state, and federal agencies, the project team is working to create a comprehensive flood management strategy. This plan will detail recommendations for decreasing flood damage, and the study can also be used for improving water quality, reducing soil erosion, and restoring fish and aquatic habitats.
Participation in the two-year project has been a valuable learning opportunity for the graduate students who have supported the research process.
“This project funded part of the students’ graduate study,” said Benjankar, “But, more importantly, it provided them with valuable experiences on process-based modeling for watershed management to tackle real-world problems. Perhaps most important of all, the project also allowed the students to contribute to work that will ultimately improve the quality of life for those living in the region.”

Scroll for the full story
Scroll for the full story
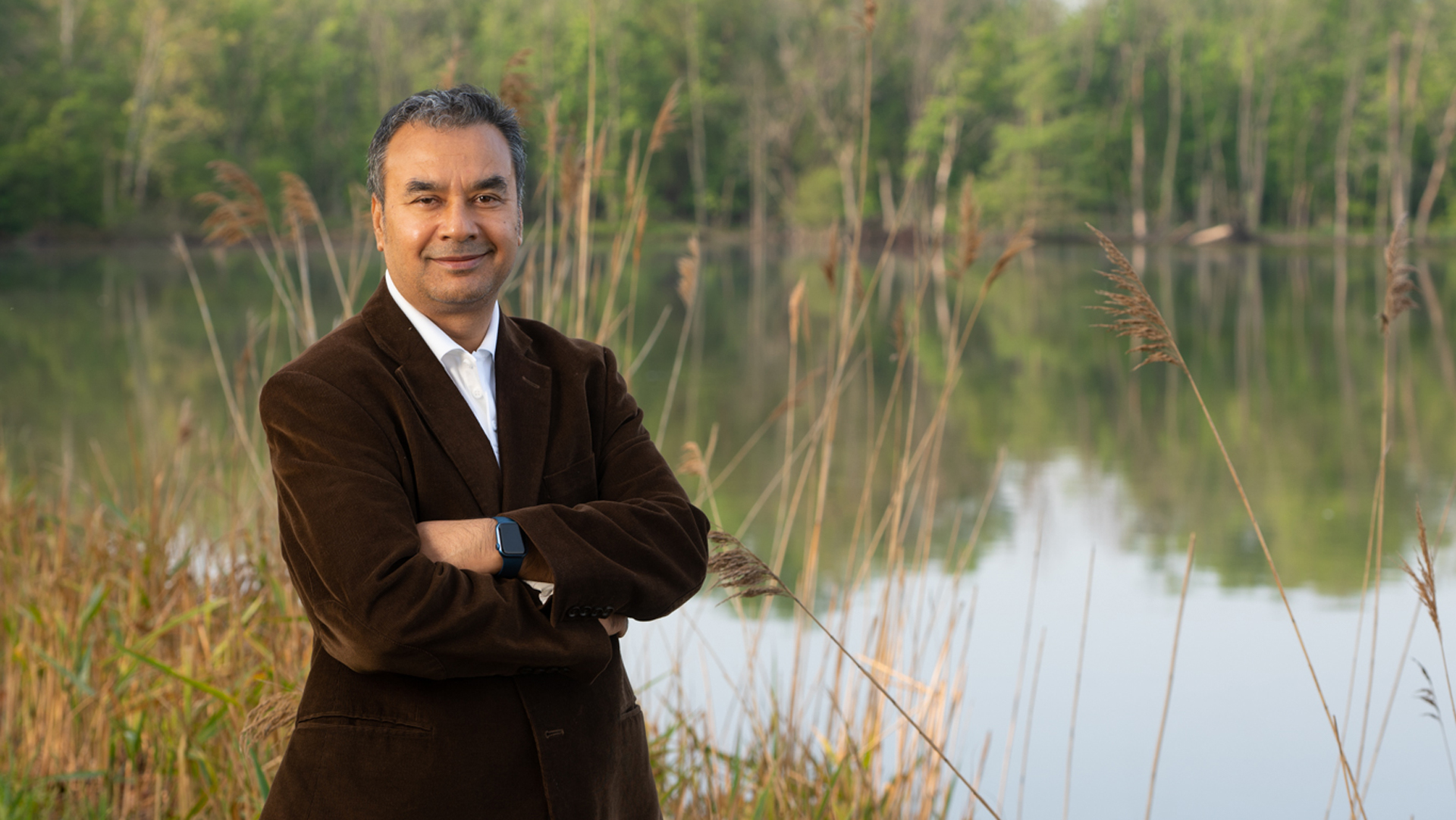
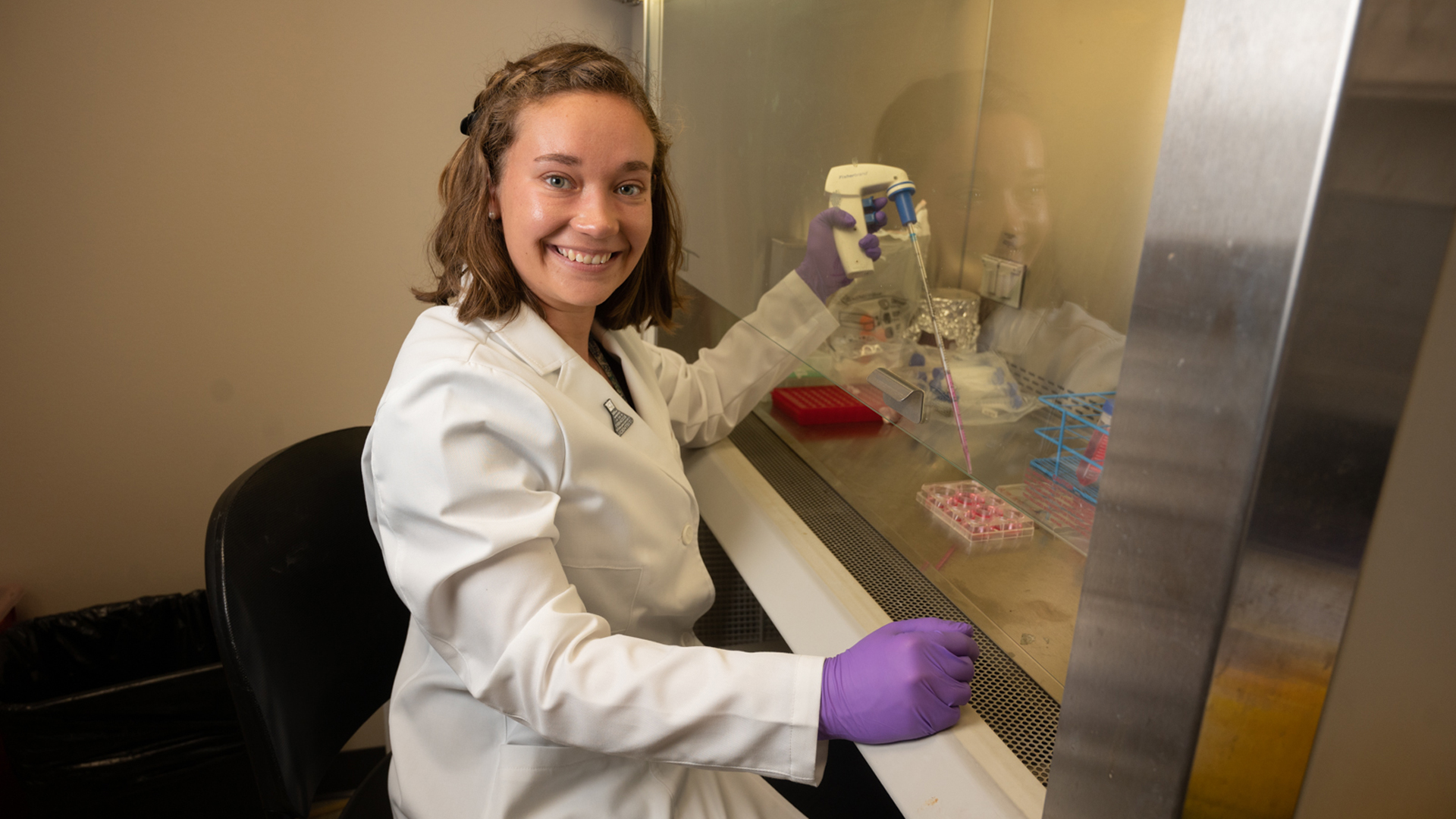
An estimated 6.7 million Americans age 65 and older are living with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) according to the Alzheimer’s Association. AD is a brain disorder that leads to progressive memory loss and cognitive decline. It is the most common type of dementia and the seventh leading cause of death in the U.S.
“Nearly everyone knows someone who is affected by AD, but there is no medication available today that can reliably treat the disease,” said Ariel Magee, who is currently studying the disease as part of the Doctor of Philosophy in pharmacology and neuroscience co-op program between SIUE and the SIU School of Medicine.
The few therapeutic options for AD only temporarily treat or slow down the symptoms of the disease. Magee’s research is focusing on drug discovery and development, specifically using a novel σ1/σ2 receptor modulator known as BBZI, which was created by Michael Crider, PhD, chair and professor of pharmaceutical sciences.
“My investigations assess BBZI across behavioral animal models to determine the effects on learning, memory, anxiety and general motor movement in an AD-mouse model,” explained Magee. “This work coincides with biochemical analyses of key brain tissues involved in these behavioral responses, as well as AD pathology.”
“Initial evaluations identify an enhancement of learning and memory with BBZI dosing,” Magee continued. “With the initial animal testing performed, I am now advancing into cellular models to delineate biochemical pathways of effect respective to BBZI, with focus on neuroinflammatory and oxidative stress markers.”
Magee began her research alongside Ken Witt, PhD, professor of pharmaceutical sciences, in 2021 and expects the project to continue for at least two more years in order to make adjustments along the way.
“The σ-receptor field has been rapidly growing, with a significant push for new drug candidates able to modulate these receptors,” said Witt. “A dual-receptor modulator has great potential, and Ariel’s work will add substantially to the field.”
Magee hopes her research will clarify the actions of sigma receptors as a target for treatment of AD and eventually lead to human trials.
“When asked about what I do in school, nearly everyone has a story about a family member or relative who is affected by AD,” added Magee. “While the disease is devastating and the stories are emotionally difficult to hear, it helps me keep in perspective the importance of my lab work and moving forward with the project to find a better treatment option.”
Using the auxin-producing bacteria, he conducted growth studies to observe their impact on seed germination and development. Research results include:
Funding from the Illinois Native Plant Society bolstered Pyles’ research which challenges the widely-accepted belief that orchid germination is dependent on fungi to provide the necessary carbohydrates for pre-photosynthetic development. Existing data between bacteria and orchids are not well characterized. Pyles results provide another stepping stone for potential in vitro conservation of these vulnerable Illinois species.
“We have limited knowledge of the identity, function and interactions of microbiomes associated with orchids,” said Pyles’ faculty mentor Betsy Esselman, PhD, professor of biological sciences. “Studies like this, identifying bacterial species present, are essential first steps to developing successful conservation strategies.”


Scroll for the full story
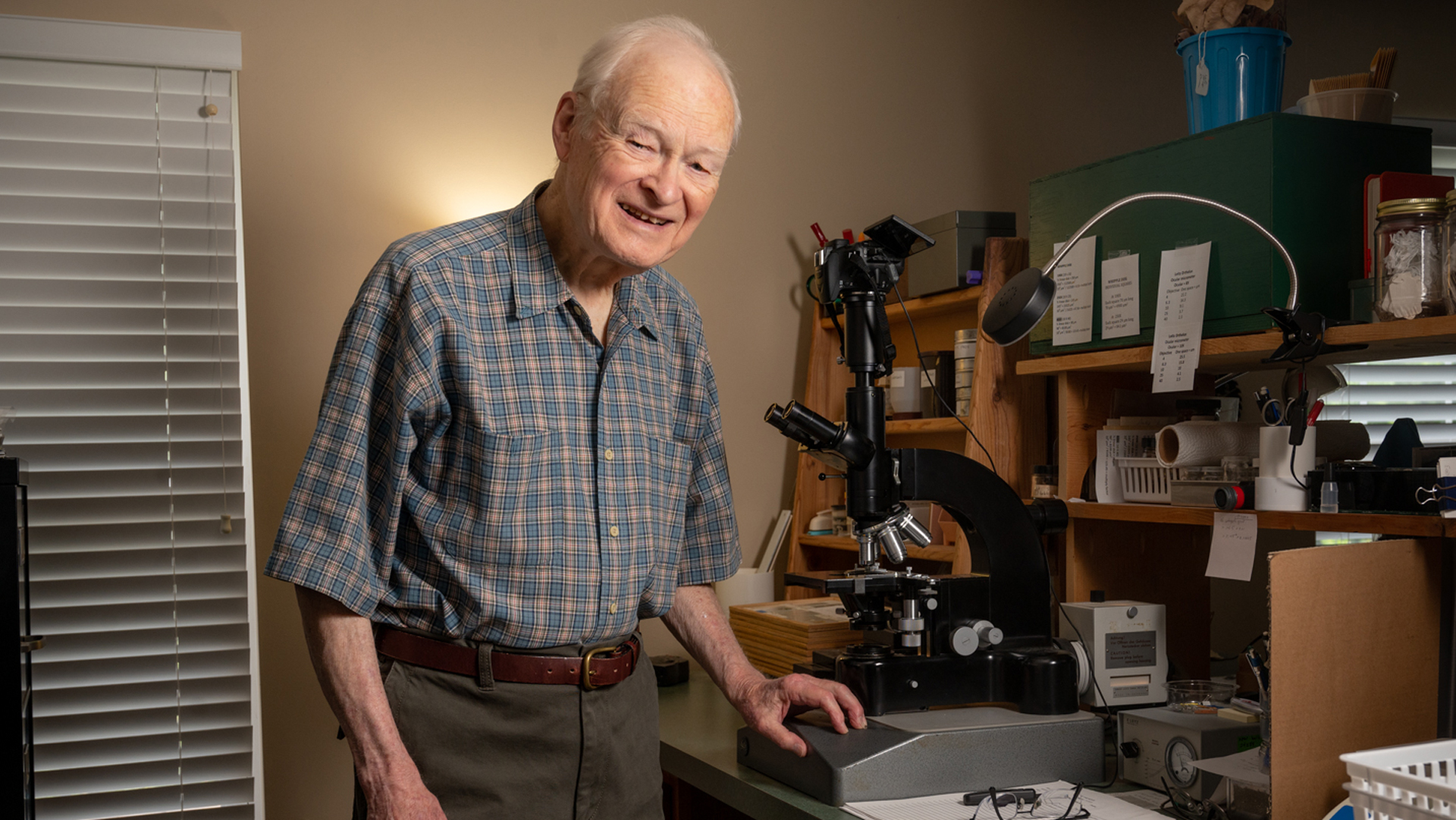
Most are aware of the services provided by leaves, first for their role in making plants grow, but even more for us, their removal of carbon dioxide from our warming atmosphere. Numerous adaptations make all this possible. Leaves breathe in two directions: absorbing carbon dioxide for photosynthesis while they release water vapor, which arrives into leaves after transporting minerals from the roots, thereby supporting all growth and maintenance. This atmospheric transfer is facilitated by tiny pores called stomates, which in oaks occur on the lower leaf surface.
My research studies some of the structural adaptations that vary in plant species as these processes take place. Working mostly with white oak (Quercus alba), I have made some interesting observations, not previously described in this species.
To get into the weeds, er trees, a bit, one can observe that seedlings or understory saplings have the largest leaves, broad with shallow sinuses between the lobes. This gives them a greater chance to capture sunlight flecks that occasionally pass through the shade. High in the canopy, the leaves are exposed to light for hours, are much smaller, and have deeper sinuses between narrow lobes. Well understood by now is that this deep lobing assists greatly in cooling by increasing air turbulence around the leaf.
For this species I have discovered that the frequency of stomates per square millimeter varies by leaf shape and size significantly. Small canopy leaves often have over 1,000 stomata per square millimeter while larger leaves of the understory have significantly fewer stomatal counts. So, why don’t the canopy leaves dry out and die faster? I’ve also found that the interior photosynthetic cells, called the mesophyll, are much denser in canopy leaves. This reduction in air space results in resistance to excess water loss.
At least for me, it gets more interesting. The network of veins or vascular bundles — that transport water upward from the roots and manufactured sugars downward — is different in many canopy tree species. Their unusual structure isolates the interior spaces (areoles) into nearly independent neighborhoods. There are multiple advantages. The leaves are stronger, thereby resisting high physical stress. Also, insect or fungal damaged areas are isolated from adjacent areoles.
Many questions remain. The work appeals to my interest in visiting mature woodlands and then preparing specimens for the microscope in laboratory space. A great match for enjoying a life in natural history.

Scroll for the full story
SIUE in Autonomous Vehicle Project for NSF Engines Development Award
SIUE is a key partner with Governors State University, in collaboration with the Illinois Innovation Network, in receiving one of the first National Science Foundation's Regional Innovation Engines (NSF Engines) awards to lead the Advancing Smart Logistics team in an effort to lay the foundation to make Illinois one of the nation’s most advanced transportation and logistics hubs. The $1 million NSF award supports a two-year planning phase to create connections and develop local innovation ecosystems, with the goal of preparing a strong proposal to become an NSF Engine and receive up to $160 million to positively impact Illinois’ economy, accelerate technology development, address societal challenges and ensure equity for those in underserved communities, advance national competitiveness, and create good-paying, local jobs.
Early Childhood Center Awarded Grant for Student-Parents
The U.S. Department of Education’s Child Care Access Means Parents in School (CCAMPIS) program has awarded SIUE’s Early Childhood Center (ECC) a $1.7 million four-year grant. With this grant money, the ECC will help student-parents by removing the financial and emotional burdens of child care while they are in class. The grant will support student-parent retention and graduation, all while ensuring the young children of students have exceptional childcare services on the SIUE campus. The CCAMPIS grant will serve as a reservoir of emergency money and child care for income-eligible student-parents.
School of Business Professor Published in International Journal
Shivendu Pratap Singh, PhD, assistant professor in the School of Business’ Department of Computer Management and Information Systems, has a published article in the December 2022 edition of Service Business by Pan-Pacific Business Association. The article is entitled “Overcoming bias against funding of female-led entrepreneurial initiatives: the democratizing influence of online crowdlending platforms." Singh’s article conveys the message that female entrepreneurs should not be discouraged by any bias they experience in the traditional financing environment. He describes how crowdlending platforms help entrepreneurs, especially those that are disadvantaged, in acquiring funding for their businesses.
School of Dental Medicine Professors Participate in Inclusion Research
Nathalia Garcia, DDS, MS, was invited to contribute as a lead author for a manuscript related to advancing women, parity and gender equity in a special issue of the Journal of Dental Education about Diversity, Equity, Inclusion and Belonging (DEIB). Garcia along with SIU SDM’s Debra Dixon, DMD, MSc, joined other women leaders in dental education to execute the project. The two professors, along with the other coauthors of the manuscript, were invited to present the topic at the 2022 American Dental Education Association-ADEA Diversity, Equity, Inclusion and Belonging Workshop. This special issue of the Journal of Dental Education is the latest in a series of ADEA projects aimed at bringing a sharper focus, and greater progress, to diversity and inclusion.
School of Nursing Gains Historic Grant for Mobile Health Unit
SIUE’s School of Nursing received its largest grant in history — $4 million from the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) — to develop a mobile health unit that will provide community-based services in East St. Louis, Fairmont City and surrounding communities. The four-year project is entitled, “Nurse education, practice, quality and retention-mobile health training program – WE CARE REACH: Responding, educating and advocating for community health.” Serving as an extension of the School’s WE CARE Clinic on SIUE’s East St. Louis Higher Education Campus, the mobile unit, WE CARE REACH, will offer primary and chronic care management services and will be staffed by healthcare providers and graduate nursing students. The program has several goals, but a core focus will be educating nursing students about promoting health equity and social determinants of health in a community setting.
SIUE Receives Grant for Inclusivity in STEM
The Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) has announced SIUE as a recipient of $531,600 as part of a multi-institutional $8 million grant through its Inclusive Excellence 3(IE3) initiative. SIUE is part of one of seven Learning Community Clusters that will be simultaneously pursuing three projects: faculty development, student engagement and agency, and curricular change. Through collaboration and accountability of the institutions, they will work to catalyze institutional change with respect to diversity and inclusion. The award will provide SIUE faculty the means to redesign their courses to align with principles of inclusion, as well as develop the SIUE STEM Student Ambassadors Program which allows students to work collaboratively to find practical solutions to STEM inclusion.

Scroll for the full story
Research and Creative Activities magazine brings to life faculty scholarship at SIUE, offering an inside look in a range of disciplines, from sculpture and science to economics and engineering.
Email address: siueresearch@siue.edu
UCDA Design Awards
Educational Advertising Awards
Collegiate Advertising Awards
Research & Creative Activities 20th Edition [pdf]
Research & Creative Activities 19th Edition
Research & Creative Activities 18th Edition
Research & Creative Activities 17th Edition
Research & Creative Activities 16th Edition
Research & Creative Activities 15th Edition

Scroll for the full story